What is Jidoka?

Updated: 2023-10-24
Definition of Jidoka
We can also call the concept of Jidoka automation with human intelligence, humanized automation, or intelligent automation. Jidoka is one of the main pillars of lean manufacturing and the Toyota Production System. Jidoka is important because it supports continuous improvement.
Meaning of Jidoka in Manufacturing
Jidoka means automation with a human touch. The Jidoka concept revolves around the idea of quality control and ensuring quality on routes and processes, as well as detecting where a defect in quality occurs.
Effectively Jidoka is a means of stopping any process if any unwanted irregularities happen within the process.

Want to stay up to date? Subscribe to our newsletter
Examples of common issues that may lead to a stop in the production process are:
Quality Issues
Quality issues can stop a production or manufacturing process. Stopping the production line quickly is the best way to find and fix a defect. This helps identify the problem causing the defect.
If there are quality issues, the production line will continue to process the defective article. Once processing this occurrence, we will add further value to the defective product. You must discard the entire block of material rather than just the initial faulty part when you add additional value.
Process Issues
Process issues, although less common than quality issues, can still result in production line stoppages. A problem in the manufacturing process can halt production and trigger an investigation into the main cause.
One instance of a process error could be improper handling or transportation of parts, potentially resulting in damage. This may cause problems with production and may require a break and improvements in how we transport parts and materials. Addressing any problematic process sections will contribute to the overall progress of the manufacturing lines.
Addressing these issues right when they occur and the reason why they occur is the whole purpose of the Jidoka method. It won’t be easy to solve problems as soon as they occur. Some of the more common problem-solving processes is the Plan-Do-Check-Act process, Kaizen, DMAIC, and the 8D process.
Continuing with the issue until solving it before starting production again is also common. You can see this in the above image.
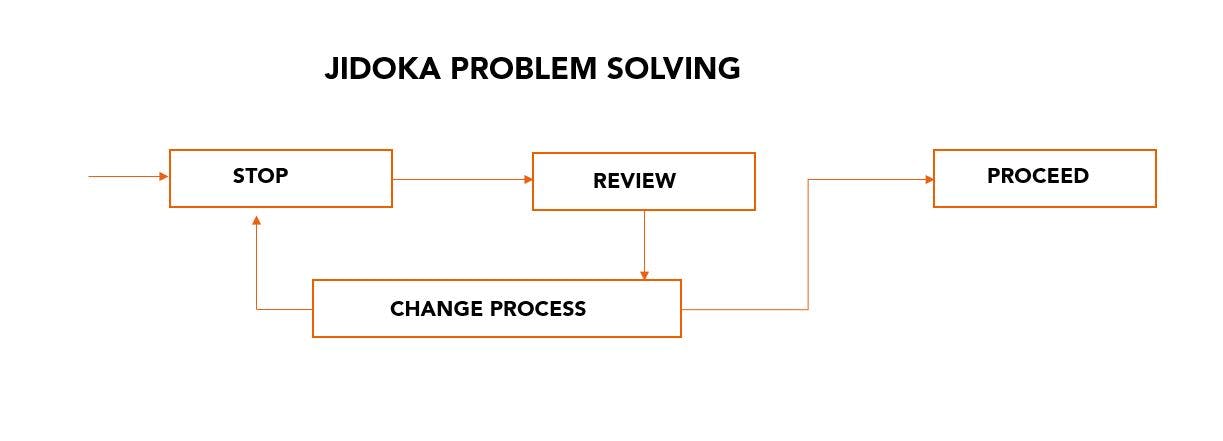
How to implement Jidoka
To ensure smooth production, it’s important to identify and fix any issues or defects early on. Proceed with production only after resolving the root cause of the problem.
Implementing Jidoka involves the following steps:
- Identify the problem or process that needs improvement: Analyze your current processes and identify areas that can benefit from automation. Look for activities that are repetitive, time-consuming, error-prone, or require manual intervention.
- Define the desired outcomes: Determine what specific goals you want to achieve through automation. Clearly define the outcomes you expect, such as increased productivity, reduced errors, improved quality, cost savings, etc.
- Select the right technology: Choose an automation technology or tool that aligns with your requirements. There are various options available, such as robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), natural language processing (NLP), etc.
- To create an automated workflow, divide the process into separate steps or tasks. You should determine the order in which to do these steps or tasks. You need to determine the inputs, outputs, decision points, and any conditions or rules that you need to apply.
- Develop the automation solution: Using the selected technology, build the automation solution that will perform the identified tasks. This may involve writing code, configuring RPA bots, training machine learning models, or creating NLP algorithms depending on the chosen technology.




